What is Trained Immunity : Innate Immunity
AUTHOR : NEHA SHARMA
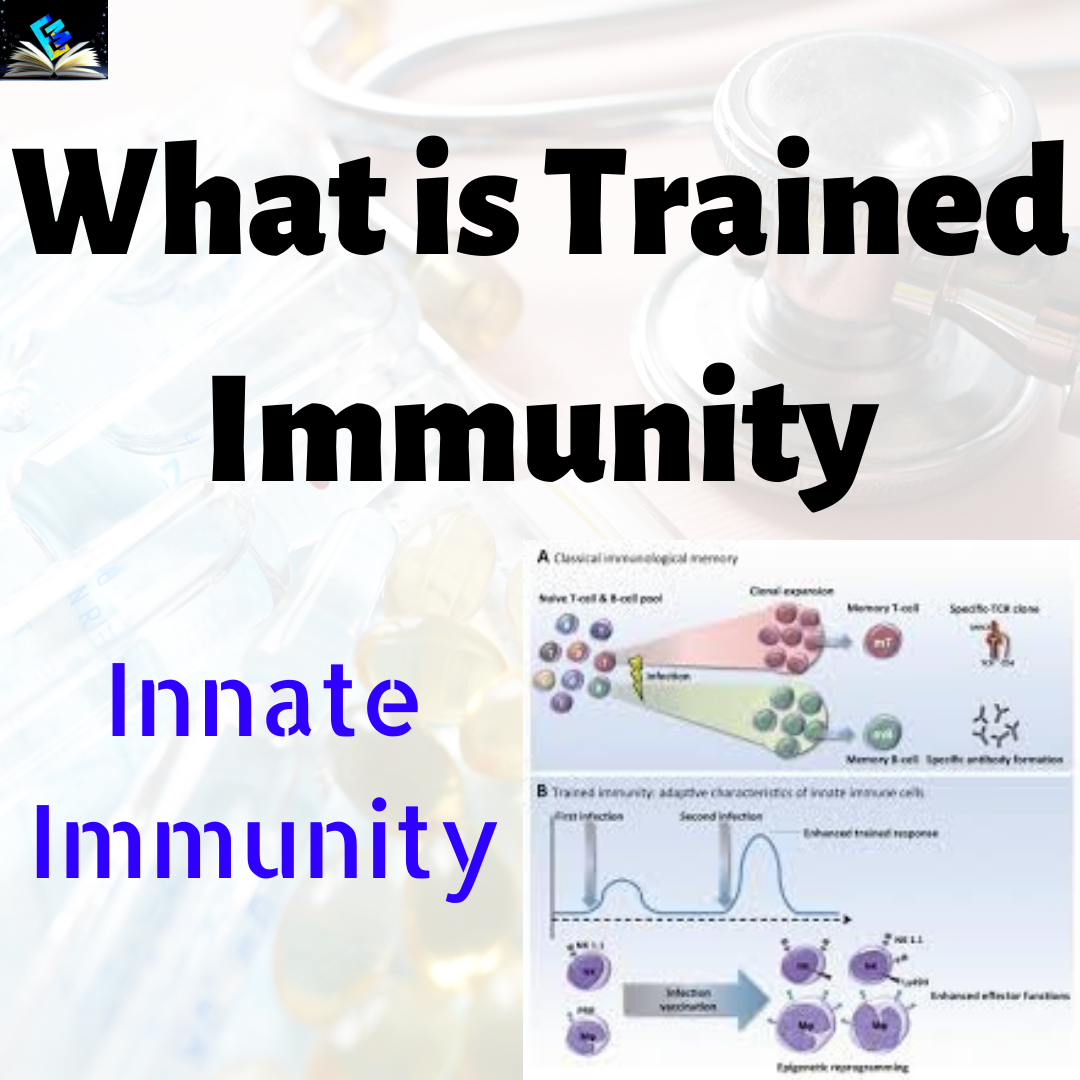
Plants and invertebrates lack an adaptive immune system, they are unable to generate memory cells after their first interaction with a foreign pathogen. Innate immune systems have undergone genetic and metabolic changes in order to cope with the challenges they face. In plants , such type of defense system is called Systemic Acquired Resistance and similar type of defense system also seen in invertebrates. So there is a term for innate immunity in vertebrates are TRAINED IMMUNITY which can be induced by different stimuli like oxidized low density Lipoprotein , vimentin etc. B and T cells can mature into memory cells that recall a pathogen and can mount a rapid response if a person is reinfected with the same disease. Innate immune cells, such as Natural Killer cells, can also mature into memory cells, forming a link between the innate and adaptive immune systems.
Stimulus for the formation of Trained Immunity
Apart from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, there is evidence that stimulants like BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin), -glucan, and lipopolysaccharides triggered a non-specific immune response against pathogens like Staphylococcus aureus, Candida albicans, and others.Humans that have been vaccinated with BCG produce more pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-). The BCG vaccine helps to reduce the rate of neonatal death. It demonstrates heterologous protection against pathogens such as Salmonella, Staphylococcus, and Herpesvirus, among others. Cross protection against pathogens from BCG heat destroyed components might persist anywhere from 2 weeks to 2 months .Basically, BCG produced NOD-2-dependent immunity. Professor Netea further claimed that if a person is vaccinated with BCG, the generated Trained Immunity will diminish or stop the multiplication of the SARS-CoV2 virus, hence reducing illness severity.
Beta -glucan induces protection against Mtb in mice via IL-1 signalling, resulting in increased survival and cytokine production due to epigenetic change in monocytes. When different innate immune cells, such as monocytes, natural killer cells, and dendritic cells, are exposed to LPS over different time intervals, the response differs.Proinflammatory responses, such as the generation of cytokines such as IFN-, occur with the first dose of LPS. TLR2/TLR4 agonist that causes hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSPC) to differentiate into monocytes and/or dendritic cells to extend the longevity of trained Immunity cells.
Different Mechanisms that induce Trained Immunity
Epigenetic Reprogramming
DNA methylation is a reversible covalent alteration of DNA that involves the insertion of a methyl-CH3 group at the 5-position of the cytosine residues, resulting in the synthesis of DNA 5-methylcytosine (5 mC). As DNA methylation patterns undergo replication and mitosis, they are passed onto the next generation by three DNA methyl transferases: DNMT1 (keep DNA methylation), DNMT3A, and DNMT3B (de novo methylation). H3K27ac (Histone 3 Lysine 27 acetylation) marks at H34Kme1 and H3K4me3 (histone 3 lysine 4 trimethylation) marks at the promoter of stimulated genes are two essential epigenetic markers for trained immunity development.Modification enzymes delete and rewrite these epigenetic marks. Histone lysine transferases (KMTs) are methylation writers, whereas histone lysine demethylases (KDMs) are methylation erasers.
Transcription of Noncoding RNA (ncRNA)
Induced trained immunity in monocytes by BCG and beta –glucan. IPLs enhance H3K4me3 tagging on immune genes in response to BCG or -glucan exposure. This epigenetic memory is subsequently transferred to HSC myeloid cells, resulting in monocytes and macrophages that have been trained. IPLs ( Immune Gene Priming LncRNA ) are UMILO IncRNAs that have been primed with Gene of Interest and produced as a product. WDR5 (WD-repeat containing protein 5) is a conserved sequence that directs MLL1 ( Mixed Lineage leukaemia protein 1) to create a complex and target genes to catalyse the trimethylation of H3K4me3 at the target gene promoter to commence transcription and generate cytokines such as IL-6 and IL-23.
Immunometabolism
There are a number of metabolic pathways that are activated by trained immunity.TCA cycle, glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation, and cholesterol metabolism are cellular metabolism pathways that are implicated in training immunity. Epigenetic alteration is used in all of these pathways to create trained immunity. In an indivior, cholesterol production and the TCA cycle are essential for the development of trained immunity. Different Pattern Recognition Receptors identify BCG, -glucans, and oxLDL (oxidised Low Density Lipoprotein), namely NOD2, Dectins, and TLR4 .The cellular metabolism shifts from oxidative phosphorylation to aerobic glycolysis as a result of these stimuli. This shift is mediated by Akt (Protein Kinase B), which regulates biological activity of proteins by phosphorylation of specific amino acids, mTOR (Mammalian Target of Rapamycin), which activates the insulin receptor, and Hypoxia –inducible factor 1 (HIF1-), which aids in the maintenance of Homeostasis and ultimately leads to increased or enhanced metabolic flux towards oxidative phosphorylation.
Different Diseases and Trained Immunity
As a result of our modern lifestyle, sickness has grown more lethal as a result of a weakened immune system. As a result, trained immunity is an essential factor in reducing the long-term effects of disease.Trained immunity stimulates the immune system to kill malignant cells or produce cytokines like IL-6 and TNF to prevent cancers like breast cancer from spreading. A western-style diet, which is dependent on the NLRP3 inflammasome, develops trained immunity in a mouse model of atherosclerosis. This happens at the level of granulocyte-monocyte precursors and lasts for months. Excessive low doses of Lipopolysaccharide in peripheral blood enhance the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and TNF- and anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10 in the brain at first, but it develops tolerance in microglia after a while and causes dementia.
Trained Immunity is a novel word in immunology; as we know, trained immunity refers to increased innate immune cell response. However, there is a process known as immunological tolerance that works in the opposite way as stimulants do to establish innate memory. Second, vaccines based on the principle of trained immunity, such as recombinant BCG vaccines containing any antigen from a novel pathogen, may provide cross protection against that disease as well. As we know, trained immunity has a memory for a specific period of time. We want to see if we can make it last longer by using vaccines, and if it can be passed down to future generations.
FOR MORE INFORMATION VISIT OUR SITE






