Rheumatoid Arthritis – Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
> What is Rheumatoid Arthritis (R.A)?
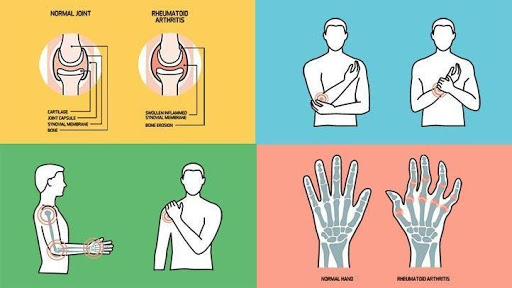
- It is a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting many joints.
- It is autoimmune disease.
- Cause joint pain and damage on both sides ( this is the one way by which doctors distinguish R.A from other forms of arthritis).
> What are the symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis(R.A)?
- Common symptoms are fatigue, weight loss, fever, bumps under skin.
- They occur during periods called flares and remission.
- Flares include:
1. Include intense stiffness in joints.
2. Pain throughout the entire body.
3. Swelling
4. Flu-like symptoms.
- Duration and intensity of flares vary interfering with everyday tasks.
- Preventing flares is a better strategy than treating them.
- Remission is a period when symptoms disappear completely.
> What is the diagnosis of R.A?
- Looking for swelling and redness.
- Examining joint function and range of motion.
- Touching affected joints to check for warmth and tenderness.
- Testing reflexes and muscle strength.
- Certain imaging tests: Ultrasound, X-ray or MRI
- Certain blood tests:
1. Rheumatoid factor test ( R.F blood test ) – checks for protein called rheumatoid factor.
2. Anti Citrullinated protein antibody test (Anti CCP) – tests antibodies associated with R.A.
3. Antinuclear antibody test – tests the immune system to see if it is producing antibodies.
4. ESR (Erythrocyte sedimentation rate) – determine the degree of inflammation in our body.
5. C-reactive protein test – a severe infection or significant inflammation anywhere in our body can trigger our liver to make C-reactive proteins.
> What is the treatment for R.A?
- Medications:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Corticosteroids
- Acetaminophen
- Disease – Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARD’s) – Blocks our body immune system response and slows down progression of R.A.
- Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitors – Prevent inflammation and stop damage to joints.
- Enough rest
- Exercise
- Apply heat or cold
- Assistive devices:
- Splints and Braces – Hold joints in resting position and reduce inflammation.
- Canes and Crutches – Maintain mobility even during flares.
- Diet:
- Anti-inflammatory diet
- Food rich in omega-3 fatty acids like chia seeds, flex seeds, walnuts and fatty fish like salmon, tuna, etc.
- Antioxidants like vitamin A, C & E and selenium found in berries, dark chocolate, spinach, kidney beans, etc.
- Lots of fiber.
- Flavonoids (soy product, green tea, grapes, etc)

“To ensure good health: eat lightly, breathe deeply, live moderately, cultivate cheerfulness, and maintain an interest in life.”
-William Londen
For more information Visit Our Site
To submit your work Contact US






